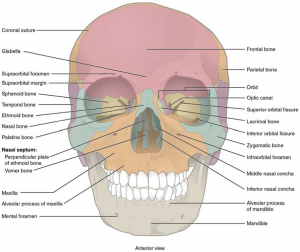
The Skull is formed by different bones kept together by Sutures. The narrow gap between the bones is filled with dense, fibrous connective tissue that unites the bones. The long sutures located between the bones of the brain case are not straight, but instead follow irregular, tightly twisting paths. These twisting lines serve to tightly interlock the adjacent bones, thus adding strength to the skull for brain protection.
The two suture lines seen on the top of the skull are the coronal and sagittal sutures. The coronal suture runs from side to side across the skull, within the coronal plane of section (Picture 1). It joins the frontal bone to the right and left parietal bones. The sagittal suture extends posteriorly from the coronal suture, running along the midline at the top of the skull in the sagittal plane of section (Picture 2). It unites the right and left parietal bones. On the posterior skull, the sagittal suture terminates by joining the lambdoid suture. The lambdoid suture extends downward and laterally to either side away from its junction with the sagittal suture. The lambdoid suture joins the occipital bone to the right and left parietal and temporal bones. This suture is named for its upside-down “V” shape, which resembles the capital letter version of the Greek letter lambda (Λ). The squamous suture is located on the lateral skull. It unites the squamous portion of the temporal bone with the parietal bone (Picture 1). At the intersection of four bones is the pterion, a small, capital-H-shaped suture line region that unites the frontal bone, parietal bone, squamous portion of the temporal bone, and greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It is the weakest part of the skull. The pterion is located approximately two finger widths above the zygomatic arch and a thumb’s width posterior to the upward portion of the zygomatic bone.
Visible from the side
- Coronal Suture: between the frontal and parietal bones
- Lambdoid Suture: between the parietal and occipital bones and continuous with the occipitomastoid suture
- Occipitomastoid Suture: between the occipital and temporal bones and continuous with the lambdoid suture
- Sphenofrontal Suture
- Sphenoparietal Suture
- Sphenosquamosal suture
- Sphenozygomatic Suture
- Squamosal Suture: between the parietal and the temporal bone
- Zygomaticotemporal Suture
- Zygomaticofrontal Suture
Visible from the front or above
- Frontal suture – Metopic suture: between the two frontal bones, prior to the fusion of the two into a single bone
- Sagittal Suture: along the midline, between parietal bones
Visible from below or inside
- Frontoethmoidal Suture
- Petrosquamous Suture
- Sphenoethmoidal Suture
- Sphenopetrosal Suture